The Elliott Wave Theory is named after Ralph Nelson Elliott. Inspired by the
Dow Theory and by observations found throughout nature, Elliott concluded that
the movement of the stock market could be predicted by observing and identifying
a repetitive pattern of waves. In fact, Elliott believed that all of man's
activities, not just the stock market, were influenced by these identifiable
series of waves.
With the help of C. J. Collins, Elliott's ideas received the attention of Wall
Street in a series of articles published in Financial World magazine in 1939.
During the 1950s and 1960s (after Elliott's passing), his work was advanced
by Hamilton Bolton. In 1960, Bolton wrote Elliott Wave Principle--A Critical
Appraisal.
This was the first significant work since Elliott's passing. In 1978, Robert
Prechter and A. J. Frost collaborated to write the book Elliott Wave Principle.
Interpretation :
The underlying forces behind the Elliott Wave Theory are of building up and
tearing down. The basic concepts of the Elliott Wave Theory are listed below.
* Action is followed by reaction.
* There are five waves in the direction of the main trend followed by three
corrective waves (a "5-3" move).
* A 5-3 move completes a cycle. This 5-3 move then becomes two subdivisions
of the next higher 5-3 wave.
* The underlying 5-3 pattern remains constant, though the time span of each
may vary.
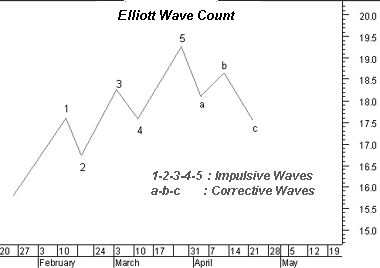
The basic pattern is made up of eight waves (five up and three down) which
are labeled 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, a, b, and c on the following chart.

Waves 1, 3, and 5 are called impulse waves. Waves 2 and 4 are called corrective
waves. Waves a, b, and c correct the main trend made by waves 1 through 5.
The main trend is established by waves 1 through 5 and can be either up or
down. Waves a, b, and c always move in the opposite direction of waves 1 through
5.
Elliott Wave Theory holds that each wave within a wave count contains a complete
5-3 wave count of a smaller cycle. The longest wave count is called the Grand
Supercycle. Grand Supercycle waves are comprised of Supercycles, and Supercycles
are comprised of Cycles. This process continues into Primary, Intermediate,
Minute, Minuette, and Sub-minuette waves.
Fibonacci numbers provide the mathematical foundation for the Elliott Wave
Theory. Briefly, the Fibonacci number sequence is made by simply starting at
1and adding the previous number to arrive at the new number (i.e., 0+1=1, 1+1=2,
2+1=3, 3+2=5, 5+3=8, 8+5=13, etc.). Each of the cycles that Elliott defined
are comprised of a total wave count that falls within the Fibonacci number
sequence. For example, the preceding chart shows two Primary waves (an impulse
wave and a corrective wave), eight intermediate waves (the 5-3 sequence shown
in the second and third charts), and 34 minute waves (as labeled). The numbers
2, 8, and 34 fall within the Fibonacci numbering sequence.
Elliott Wave practitioners use their determination of the wave count in combination
with the Fibonacci numbers to predict the time span and magnitude of future
market moves ranging from minutes and hours to years and decades.
There is general agreement among Elliott Wave practitioners that the most recent
Grand Super cycle began in 1932 and that the final fifth wave of this cycle
began at the market bottom in 1982. However, there has been much disparity
since 1982. Many heralded the arrival of the October 1987 crash as the end
of the cycle. The strong recovery that has since followed has caused them to
reevaluate their wave counts. Herein, lies the weakness of the Elliott Wave
Theory--its predictive value is dependent on an accurate wave count. Determining
where one wave starts and another wave ends can be extremely subjective.
Elliott Oscillator
To keep tab of Elliott Wave logic, we require an indicator that measures the
rate of price change in one wave against the rate of change in another wave.
Standard indicators fail to perform this comparison. They merely compare price
against price and fail to compare the rate of price action. After years of
research, The Elliott Oscillator was developed. The idea of the oscillator
is described below.
An Elliott Oscillator is basically calculated from finding the difference between
two moving averages. If we were to use a small moving average and a large moving
average, the difference between two will show the rate of increase in prices.
The small moving average represent the current price action, while the larger
moving average represents the overall price action.
When the prices are gapping up inside a Wave 3 the current prices are surging;
the difference between the small and large moving averages is great and produces
a large oscillator value.However, in Wave 5 the current prices are not moving
up at a fast rate and, therefore, the difference between the small and large
moving averages is minimal. This produces a smaller oscillator value.
By comparing the oscillator peaks, one can distinguish between a Wave 3 and
Wave 5 phase.
Recommended small and large moving averages are 5 and 35 days relatively and the formula for Elliott Oscillator as follows: